Sugar is a double-edged sword. It can be used to add flavour and texture to foods, but consuming too much of it can lead to a number of health problems like diabetes, kidney damage, nerve damage, heart diseases, stroke and also affects your eyesight leading to permanent blindness.
In this article, you will get insights into some potential signs of consuming excessive sugar in your daily diets and a few effective ways to regulate your blood sugar levels.
Potential signs of consuming too much sugar
1. Increased appetite and weight gain
Consuming too much sugar results in increased appetite and weight gain. Sugar is a very energy-dense food. Eating lots of sugar can cause you to overeat because the sugar hides in many foods. Sugar is directly associated with obesity and weight gain because it is hard to consume too much sugar if you are eating whole foods that contain no added sugar.
If you are facing health issues due to intake of excessive sugar in your diet then consider Food Psychology, Body Screening to regulate your sugar levels and keep it in control.
2. Fatigue and tiredness
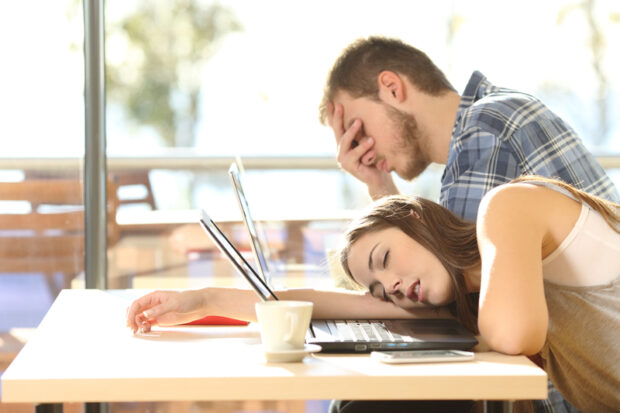

Consuming too much sugar can also cause fatigue and tiredness. A diet high in sugary foods can cause you to feel sluggish and have low energy levels. It can also lead to mood swings, because your blood sugar levels will increase quickly after consuming something high in sugar, and then crash later on, making you feel tired and irritable.
3. Increased cravings for sweets
Consuming too much sugar causes your body to become used to the sweet taste. This might seem like a no-brainer for those who have experienced it. This causes your brain’s reward centre to crave more sweet treats when your blood sugar level dips below a certain point, making it harder to resist those sweet temptations in the future. Soon it will turn into a vicious cycle even before you notice it
4. Oral diseases and tooth decay
Consuming excessive sugar can also result in oral diseases like gingivitis and gum disease which can lead to tooth decay. It disrupts your overall oral hygiene by producing enamel eating acids that can cause the formation of acids. This is extremely harmful to your teeth and might cause tooth infection if you keep eating sugary meals everyday.
5. Insomnia or sleeping problems
Consuming too much sugar can also disrupt your sleeping cycle and you may face sleeping problems. Insomnia is now common amongst people with a busy schedule but one of the major reasons for not feeling sleepy can be eating extra sugar in your daily meals. Your sleeping cycle is also determined by the glycemic control which is affected by consuming additional sugary foods.
What to do if you are consuming too much sugar
1. Exercise regularly

Exercise is one of the most important parts of managing your blood sugar. It can help you lose weight, which helps regulate your blood sugar levels. If you are overweight and have diabetes, losing weight may even mean you no longer need to use insulin!
When exercising, try to focus on low impact activities to reduce the risk of injury. Also, try to find exercises that you can do at home or in a gym, so that you don’t have to worry about weather conditions or safety.
2. Manage your diet
A healthy diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels. One way to keep them under control is by eating foods with a low glycemic index (GI), which means they won’t cause your blood glucose level to rise as quickly and stay elevated for longer periods of time than other foods with higher GI values would do.
Eating more fruits and vegetables will also help keep your blood sugar levels stable because they contain fibre, which slows down how fast sugars get absorbed into your bloodstream after digestion so it takes longer before they reach their peak level.
You should also limit your intake of refined carbs like white bread or pasta because these are high in simple starches which break down into glucose very quickly when digested
3. Drink more water and stay hydrated
Water is one of the best ways to fight off diabetes because it helps flush out excess glucose from your system. It also helps reduce inflammation throughout your body which can help with joint pain or stiffness associated with diabetes. You must also consider drinking other fluids such as herbal teas and broths, but sugar-free options are best.
To help keep your blood sugar levels more stable, you need to avoid dehydration. Reduced kidney function means that you will be more prone to dehydration and this should be avoided at all costs. Drinking plenty of water each day is a key way to stay hydrated and keep your body in balance.
4. Manage your stress levels
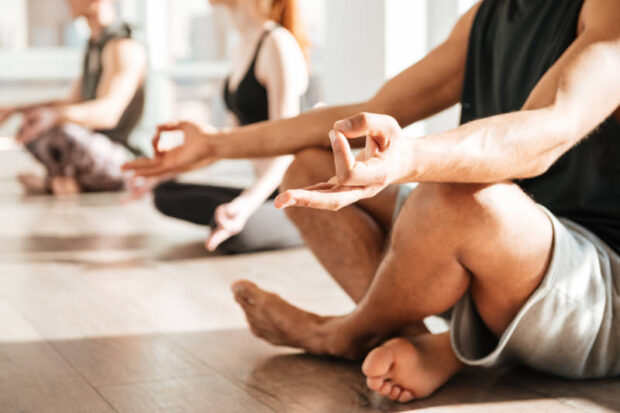

Stress can affect our blood sugar levels and this can lead to too much sugar in the bloodstream. Stress increases the amount of cortisol hormone in the body and can make blood sugar spike. The best thing you can do is get plenty of rest and manage your stress levels so that they are not too high.
Try using relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga, listening to music, going for a walk in nature or taking up a hobby that you enjoy doing to control your stress.
The Bottom-line
Too much sugar is a health hazard. The effects of consuming too much sugar are real, and they can have serious repercussions on your body and mind. When you consume too much sugar, your blood sugar levels can spike and plummet, which can be a real drag for your system.
Consuming too much sugar can lead to some awful side effects. Keep a track of these health signs that can occur due to consuming too much sugar in your daily meals. If you have high sugar levels then follow these methods to keep your sugar levels back to normal.